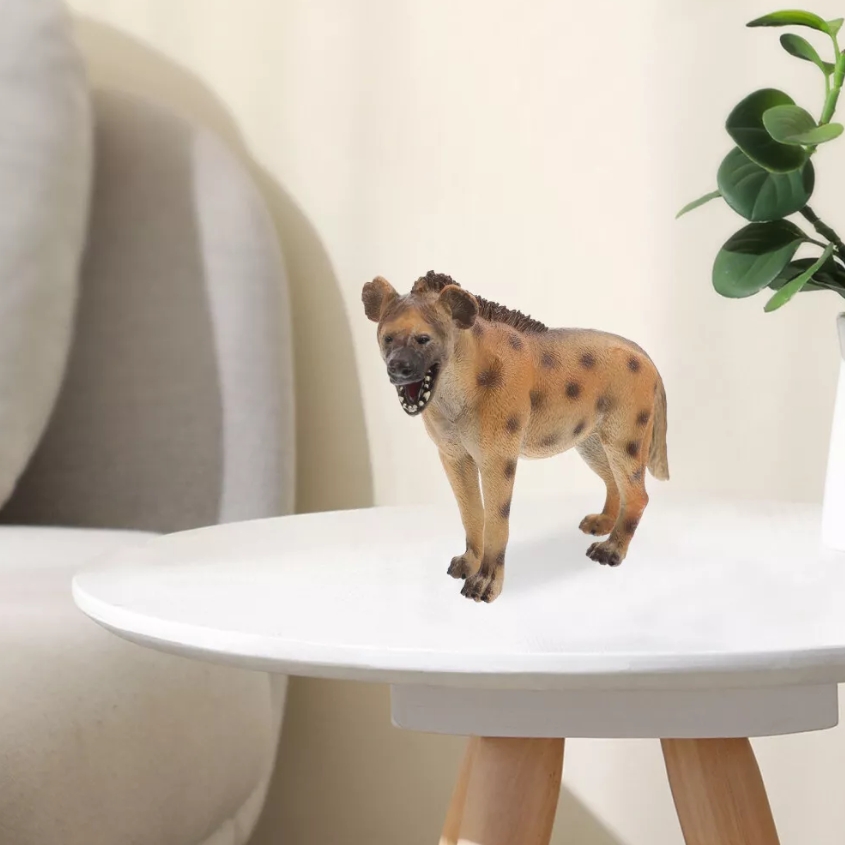
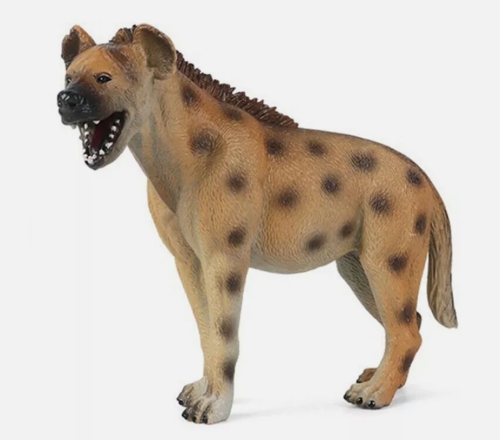
Hyenas are unique and complex animals known for their robust posture and unique social behavior. They belong to the order Carnivore, and although often misunderstood as predators, they actually play an important role in the ecosystem as scavengers.
Hyenas are large in size, have thick limbs, and powerful jaws and teeth that allow them to easily tear through the flesh of their prey. Hyenas have a more specific skull structure than ordinary canids, meaning they can withstand greater stress when hunting and eating food. In terms of predation, hyenas have a unique cooperative hunting strategy, often hunting in small groups, forming a highly coordinated team cooperation.
This animal is known for its complex social structure, and group life is an important feature. Each group is usually led by a dominant female, while the other members are responsible for guarding and raising the offspring. This social structure makes hyenas more stable in the face of competition and threats, and they will rely on each other to protect each other and share food. This spirit of cooperation allows them to survive and thrive in a highly competitive environment.
It is worth noting that hyenas are often portrayed in a negative image in culture, even as dishonorable creatures. In reality, however, their lifestyles and behaviors are complex and thought-provoking. More than just predators, hyenas are an important part of the ecosystem, playing an integral role in maintaining the ecological balance by cleaning up carcasses and helping to control prey populations.
Hyenas are also quite dramatic when it comes to mating. Female hyenas are often dominant in their groups, even in some cases more so than males. This structure gives females more opportunity to choose mates, which affects the genetic characteristics of the entire population.