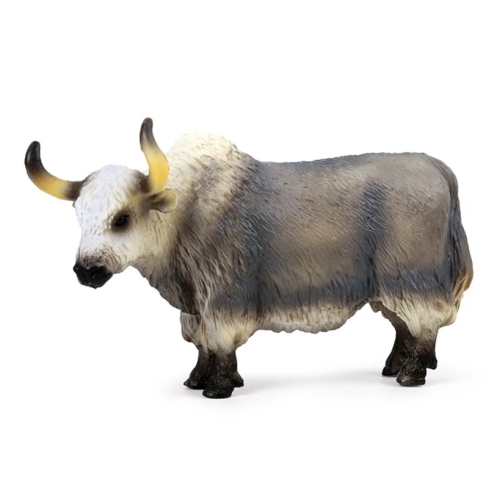
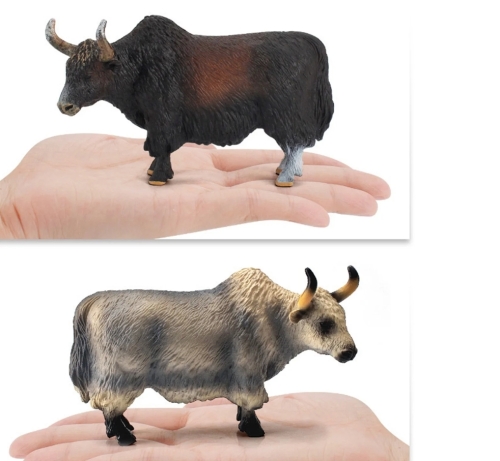
Yak model is a kind of biological model which has attracted more and more attention in modern agriculture and ecology research. Yak, as a unique highland animal, has the ability of cold tolerance, high altitude hypoxia tolerance and adaptability to harsh environment. This special biological characteristic makes yak an ideal object for studying environmental adaptability and ecological balance.
In ecological research, yak models can help us understand the impact of climate change on plateau ecosystems. Yaks have physiological and behavioral characteristics that enable them to survive food shortages and inclement weather conditions in cold climates. By studying yak survival strategies, scientists can better predict the resilience of other species and the stability of ecosystems in the context of global warming.
Yaks also play an important role in the agricultural economy. Its meat, dairy and hair are important sources of income for many people. The research on the population dynamics and reproductive behavior of yaks can provide scientific basis for breeding industry, thus improving the production performance and economic value of yaks.
Yak model also shows its unique value in genetic research. The genetic diversity and adaptability of yaks provide important clues for the study of biological evolution and speciation. By analyzing the yak genome, researchers can gain insight into the genes involved in environmental adaptation and reveal how past climate changes affected the evolution of the species.
In conclusion, the yak model provides us with a multi-dimensional research platform, which has great potential in the fields of ecology, genetics and agricultural economy. By deeply exploring this unique species, scientists can not only provide evidence for its protection and rational use, but also provide inspiration for the sustainable development of other plateau ecosystems.