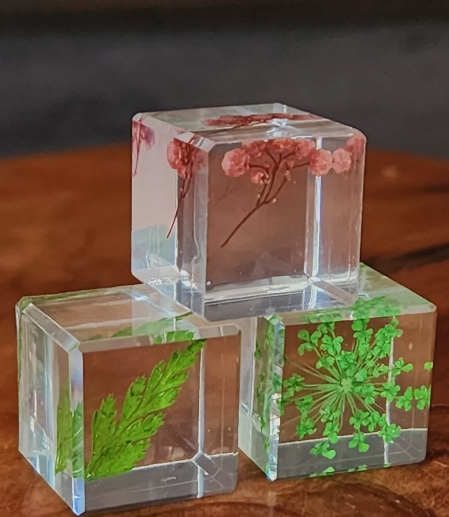
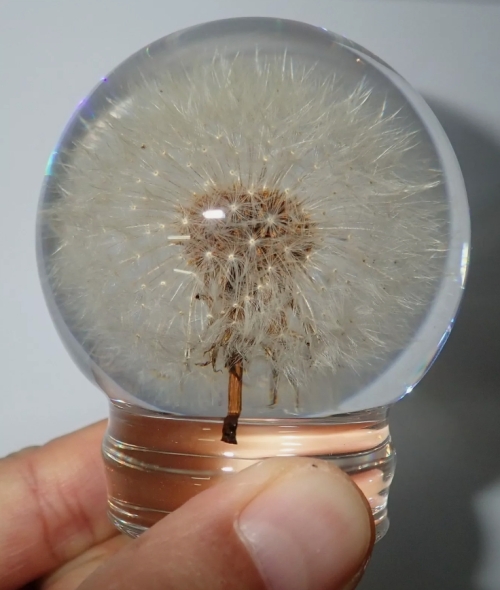
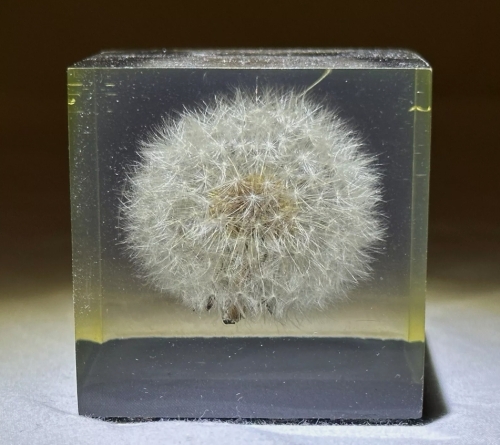
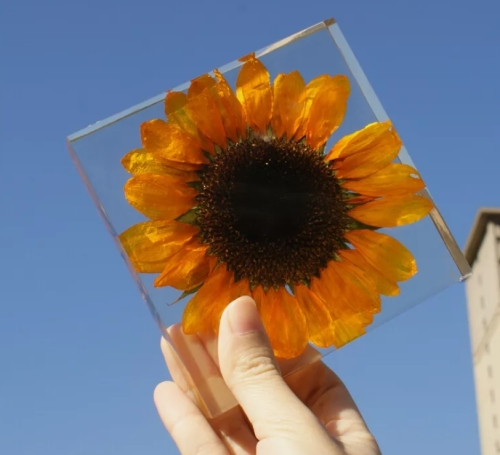
Plant specimens are examples of plant samples collected, processed and preserved in various ways for scientific research, education and display. This approach plays an important role in fields such as botany, ecology and environmental science.
The collection of plant specimens usually follows strict principles. First, healthy and mature plant individuals are selected for collection to ensure the representativeness and validity of the specimens. During the collection, interference to the ecological environment should be avoided as much as possible, and the principle of sustainable collection should be followed. In the process of collection, the growing environment of plants, collection time and other relevant ecological information are usually recorded, which is of great significance for the follow-up study of specimens.
Specimen treatment is an important step in plant specimen preparation. The collected plant samples need to be dried and pressed to prevent rot and spoilage. Usually pressed using plant specimen paper, the various parts of the plant (such as leaves, flowers, fruits, etc.) need to be taken care to maintain integrity and form. Dried specimens can be stored in a specimen box to ensure their long-term preservation.
Plant specimens are not only widely used in academic research, but also play an important role in education. Many schools and scientific research institutions will use plant specimens as teaching materials, through the observation of actual specimens, students can more intuitively understand the morphological characteristics of plants and taxonomic knowledge. In addition, plant specimens are often used in science exhibitions and museum displays to arouse public concern about plant diversity and ecological conservation.