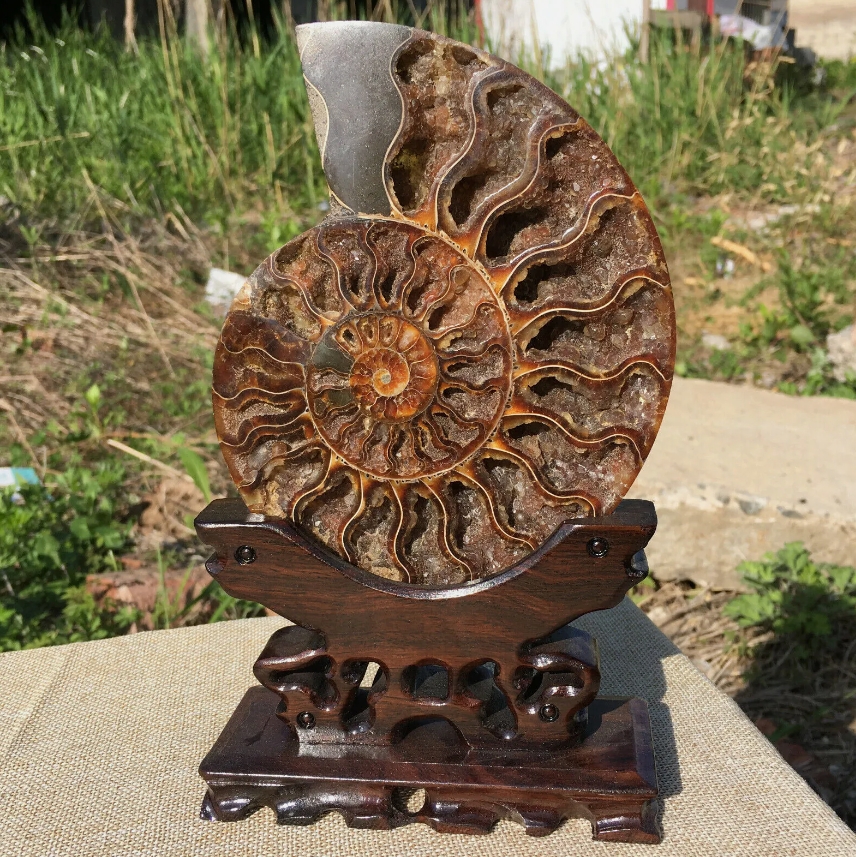
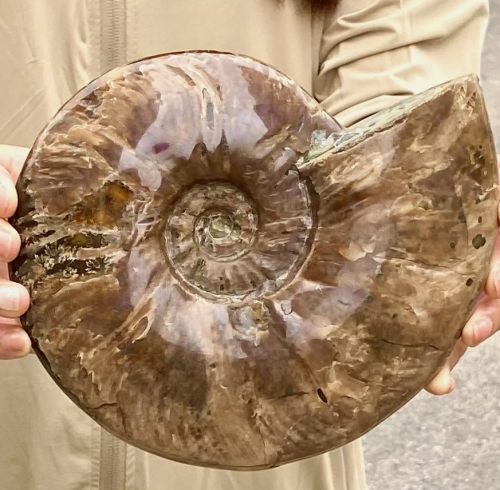
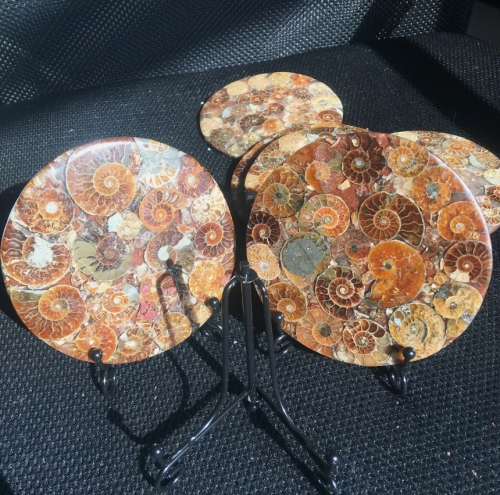
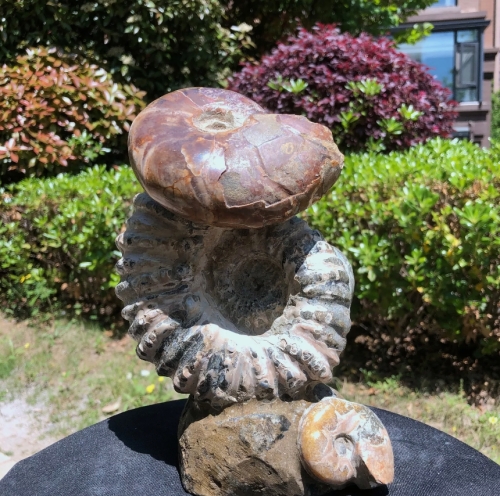
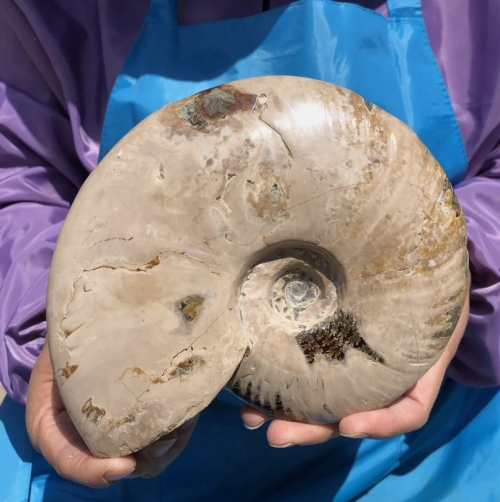
Fossil specimens are indispensable materials in geological and paleontological research, they can not only provide us with valuable information about the history of the earth and biological evolution, but also reveal the evolution and changes of ancient ecosystems. Fossils are the remains of ancient organisms, usually preserved in mineralized form, including the remains, traces, or models of animals, plants, and microorganisms. Through the study of fossil specimens, scientists can reconstruct the natural environment in the past and understand the diversity and adaptability of life.
The process of fossil formation usually takes a long time. When an organism dies, its remains are often covered with other material, such as mud or sediment. In the absence of oxygen,microbial decomposition slows down, gradually allowing the remains to be infiltrated and replaced by minerals, forming fossils. This process can take thousands or even millions of years. Ultimately,the shape and internal structure of the fossil were preserved, providing clues for future research.
There are many kinds of fossil specimens, including bone fossils, shell fossils, resin fossils and so on. Skeletal fossils can reveal the morphological characteristics and living habits of ancient animals,while plant fossils can provide information about the species and ecological environment of ancient plants. Fossilized resin, often referred to as amber, can contain valuable information such as plant pollen and cells in addition to preserving small organisms such as insects.
Through these studies, scientists can trace the evolution of living things and reveal the origin and extinction of species. For example, certain fossil specimens show migrations from aquatic to terrestrial organisms, indicating the ability of life to adapt and evolve many times on Earth.