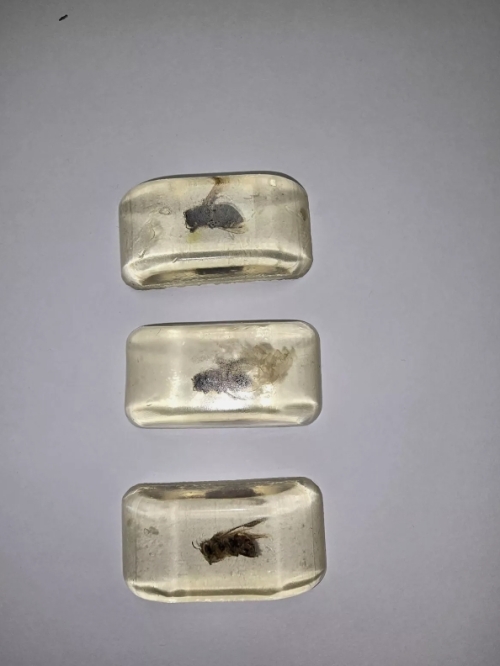
Bees, as the indispensable pollinators in nature, play an important role in the ecosystem. In the process of studying bees, the preparation and preservation of bee specimens is particularly important. Honeybee specimens not only provide valuable physical data for scientific research, but also help us better understand the biodiversity and ecological functions of honeybees.
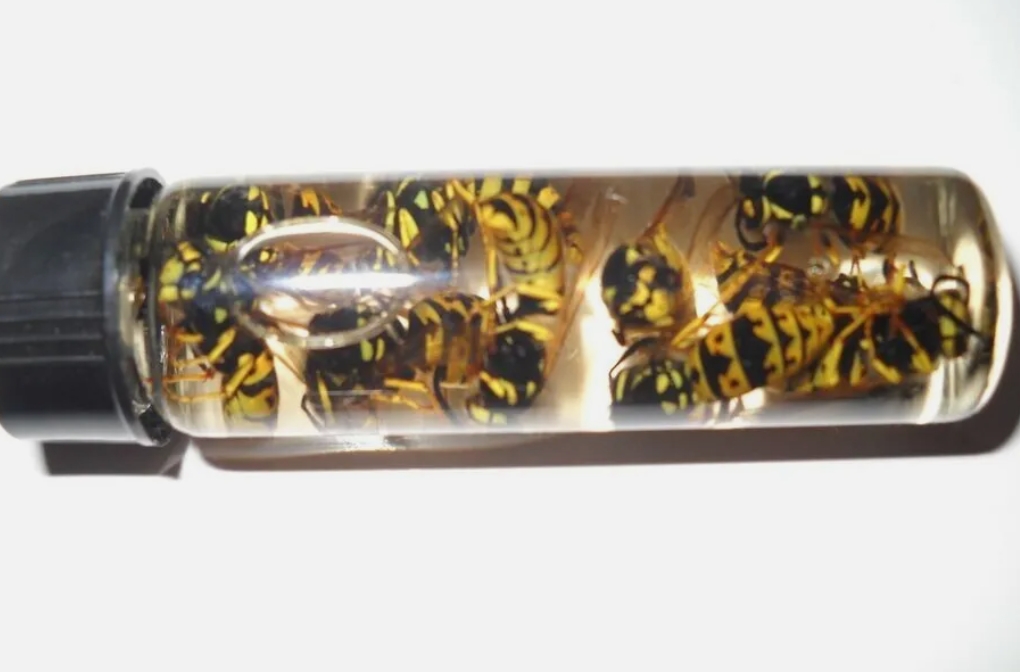
The preparation of bee specimens usually includes several important steps: collection, fixation, drying and specimen handling. First, collecting bees correctly is crucial. In order to ensure the authenticity and integrity of the sample, try to select healthy and active bee individuals. The quality of specimens can be improved by collecting at the right time and environment. Immediately after collection, the bees should be placed in a container containing a fixative, which can effectively prevent their corruption and deformation.
Once fixed, the bees need to be dried. In order to preserve the details of the bee body, air drying or freeze drying is usually used. After drying, bee specimens need to be preserved for a long time. This can be done by placing it in a dry, light-free environment and using appropriate packaging materials to avoid moisture and moth infestation.
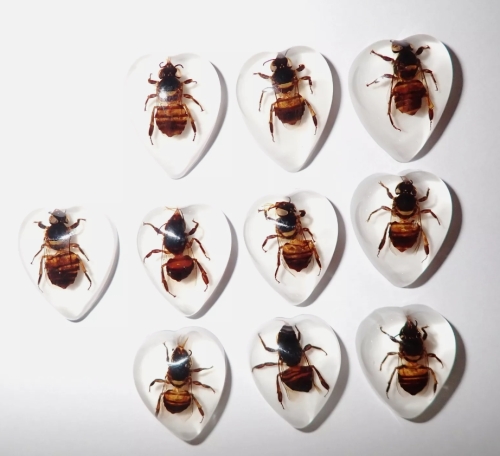
In order to make specimens more academic value, detailed label information is usually attached after specimen production, including key information such as collection location, time, gatherer name, bee species, etc. This information is not only convenient for later research and classification, but also provides an important basis for scientific communication.